
Five Causes of RespiratoryDistress in the Newborn
© William Herring, MD, FACR

Diseases
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Neonatal Pneumonia

Pre-test
Decide which of those 5 diseases isdepicted on each of the following 5chest radiographs

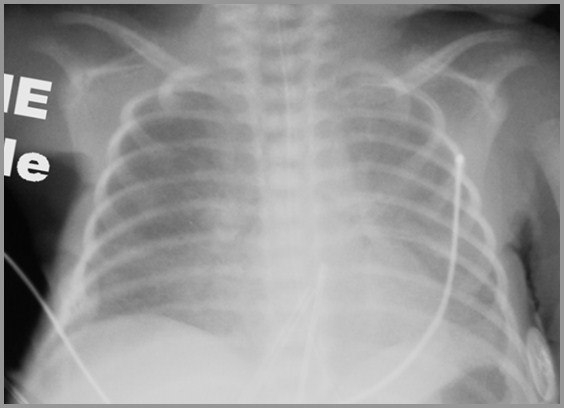
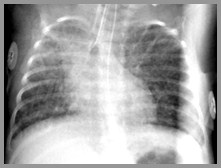
34 week preemie 6 weeks post-partum
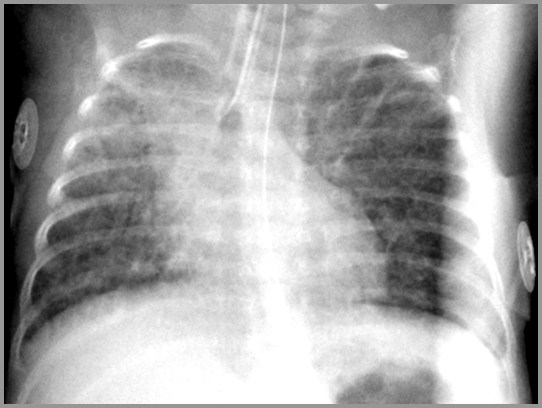

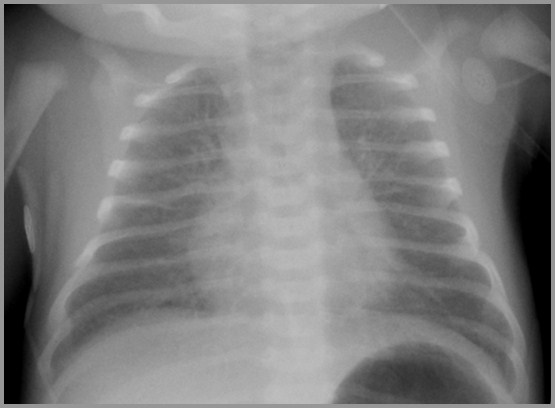
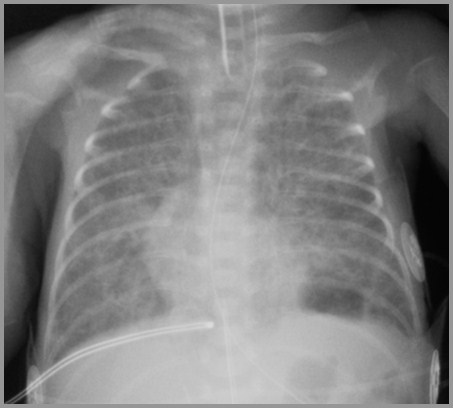
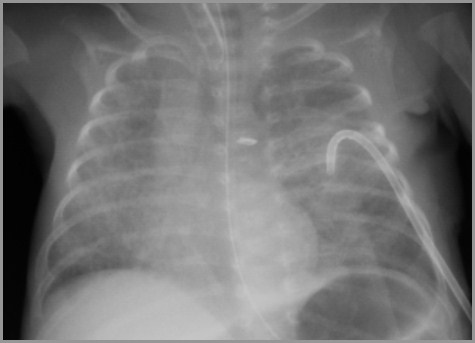
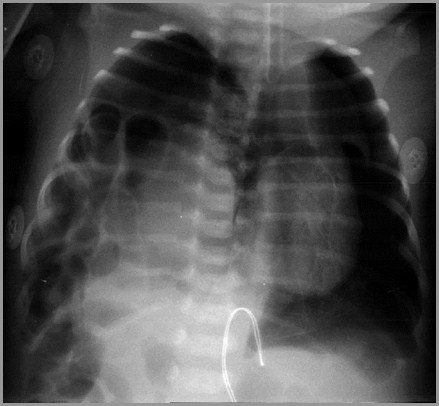
Term infant with respiratory distress; birth

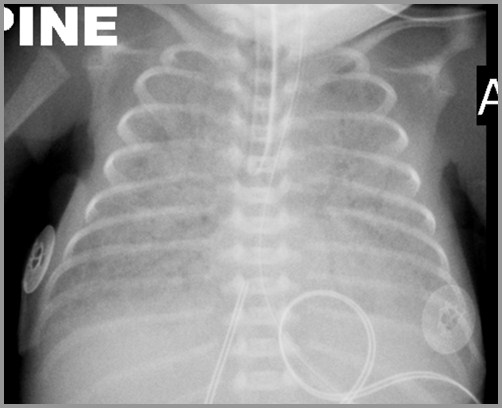
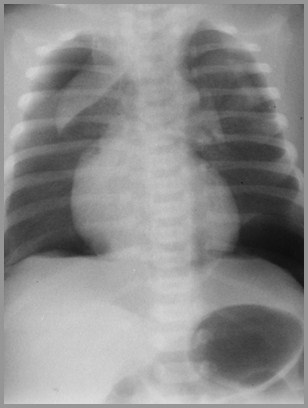
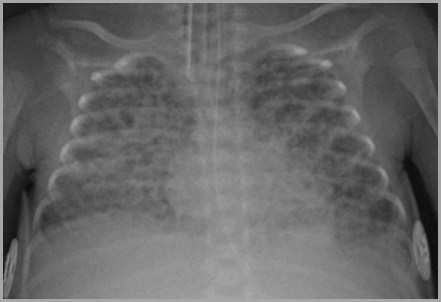
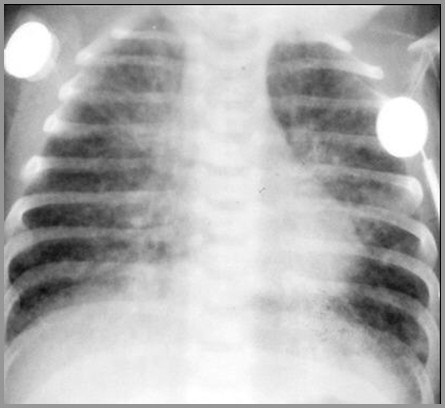
36 week preemie with respiratory distress; birth

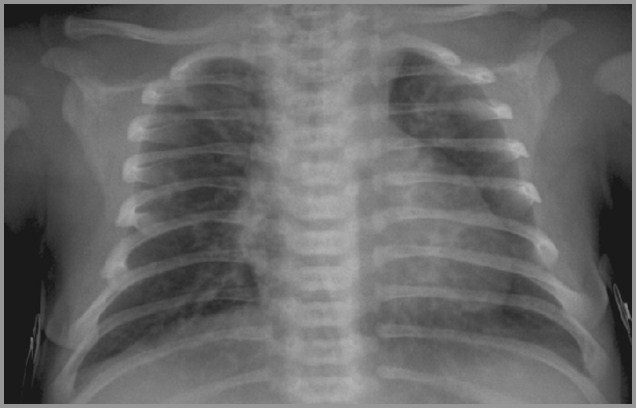
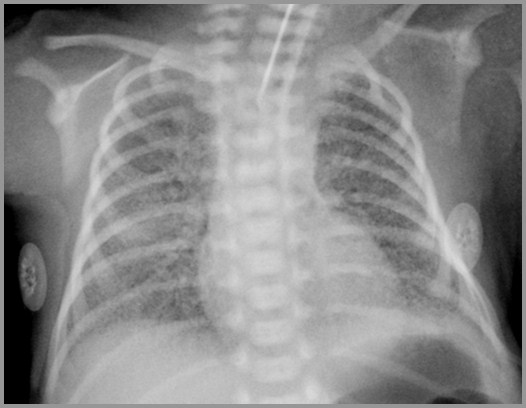
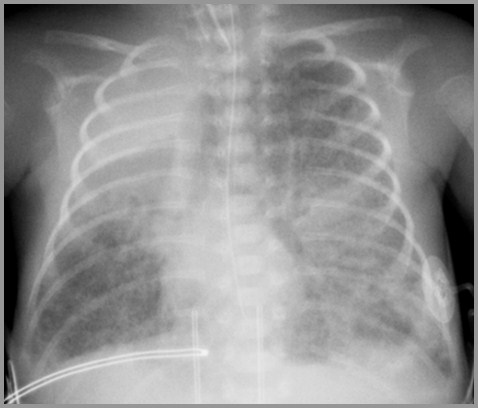
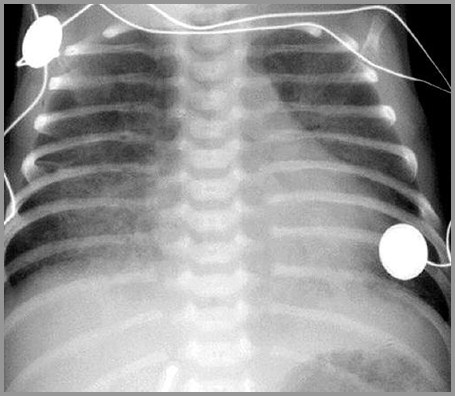
Term infant with respiratory distress; birth
USUHS

© R3
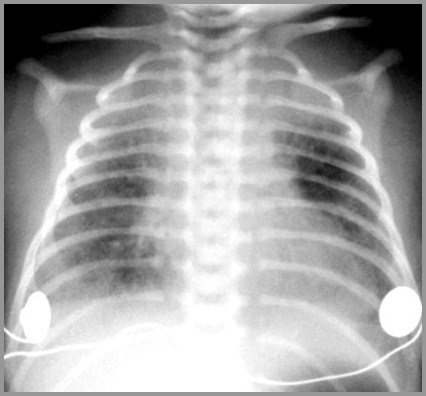
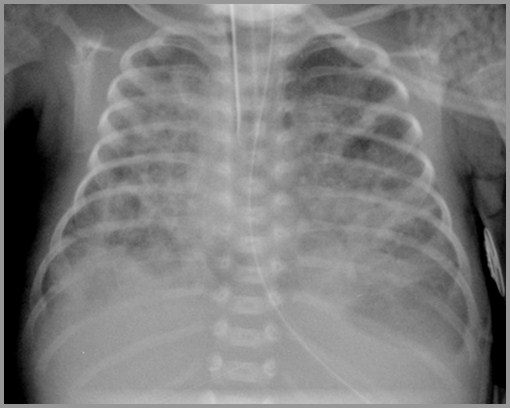
Term infant with severe respiratory distress; Day 2

Uncommon Diseases
Congenital Lobar Emphysema
Sequestration
Congenital Adenomatoid Malformation

Key History
What was the gestational age of the babyat birth?
Preemie by definition: < 37 weeks
How old is the baby?
Hours, days, weeks after birth

How old?
Proximal humeral epiphysis visible on USat 38 weeks -- relates to lung maturity
Not usually ossified at birth

Hyaline Membrane Disease
Respiratory Distress Syndromeof the Newborn
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Respiratory Distress Syndromeof the Newborn

Hyaline Membrane DiseaseGeneral Considerations
Lack of sufficient surfactant production
pressure to keep alveoli open; lungcompliance
Predisposed
Caucasian, premature infants < 34 weeks
Cesarean-section
Second-born twins
Infants of diabetic mothers
lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio in amniotic fluid

Hyaline Membrane DiseaseGeneral Considerations
Thin rim of fibrin coats terminal bronchioles andalveolar ducts
Result of, rather than cause of, this disease
Other diseases produce hyaline membranes
Meconium aspiration syndrome and BPD
Hence, AKA Respiratory Distress Syndrome ofthe Newborn

Hyaline Membrane DiseaseClinical Findings
Symptoms present in first 2 hours of life
Symptoms that begin > 8 hrs are not due toHMD
May in severity from 24 - 48 hours
Then, gradual improvement > 48-72hours

Hyaline Membrane DiseaseImaging Findings
Typically, diffuse “ground-glass” orfinely granular appearance
Bilateral and symmetrical distribution
Air bronchograms are common
Especially extending peripherally
Hypoaeration in non-ventilated lungs
Hyperinflation excludes HMD

Hyaline Membrane Disease

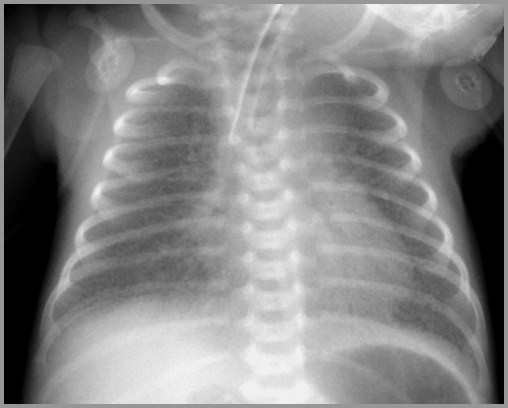
Hyaline Membrane Disease

Hyaline Membrane DiseaseImaging Findings
“Granularity” is the interplay of
Air-distended bronchioles & ducts
Background of atelectasis of alveoli
May change from film-to-film if there is
Expiration (air disappears)
Better aeration (small bubble formation)

“Pseudoclearing” of HMD Due toGreater Distension of Bronchioles and Alveolar Ducts
Birth
5 hours later

Hyaline Membrane DiseaseTreatment
Surfactant administered via ETT
Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
Continuous positive airway pressure(CPAP)
High Frequency Ventilation (HFV)
Small lung volumes at 150 breaths/min
Oxygen and diuretics

Hyaline Membrane DiseasePrognosis
In the past, almost all infants died ofHMD by 72 hrs
Therefore, complications were rare
With assisted ventilation, recovery >90%
All that follows represent complicationsof treatment, rather than of the disease




Out topleuralspace =PTX
Into lung =pneumatocoele
Alongbronchi =PIE
Out tomediastinum =pneumomediastinum
Air Leaks

Down toabdomen =pneumoperitoneum

Into pericardium = pneumopericardium
Complications of Treatment

Pneumatocoele
Pneumatocoele formation
Complications of Treatment

Hyaline Membrane DiseasePulmonary Interstitial Emphysema
Pulmonary interstitial emphysema (PIE)
Usually occurs on day 2 or 3
Earlier it occurs, more ominous the sign
Air is in lymphatics
Small bubbles, streaky appearance of air
Frequent precursor to PTX (70-80%)

Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema
Complications of Treatment

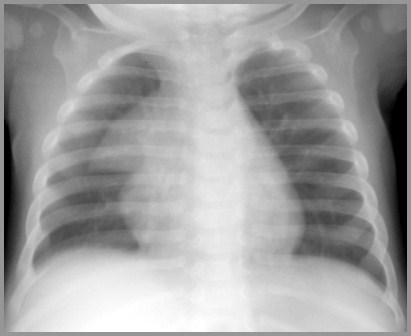
HMD with Pneumomediastinum
Complications of Treatment

Thymic Sail Signs
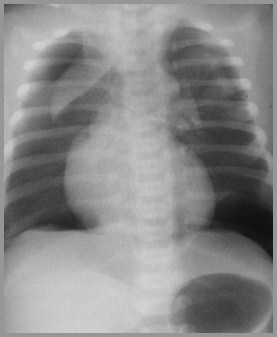
Spinnaker Sail Sign(Abnormal)
Sail Sign(Normal)
Complications of Treatment

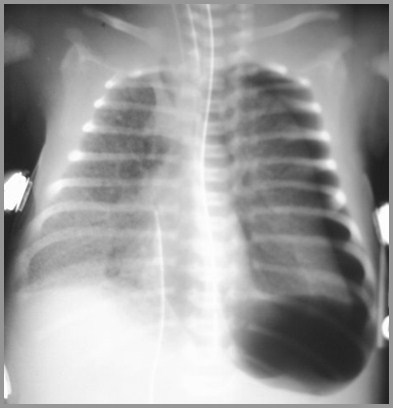
HMD with Pneumothorax
Complications of Treatment

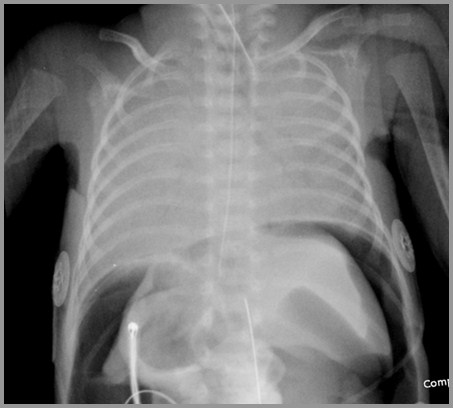
Severe HMD with Pneumopericardium
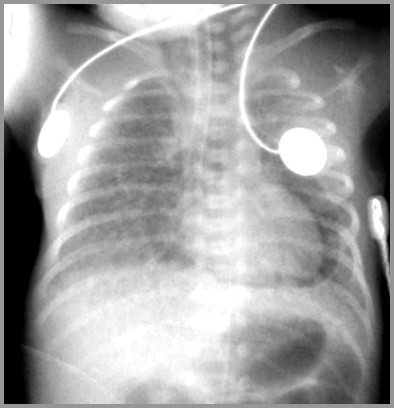
Complications of Treatment

Severe HMD with Pneumoperitoneum
Complications of Treatment

Hyaline Membrane Disease
Worsening Opacification
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Worsening Opacification

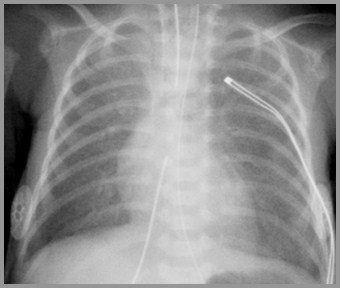
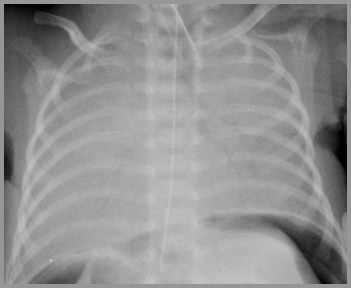
Day 4
Day 1
Worsening Opacification – Cause?
Worsening opacification

Hyaline Membrane DiseaseWorsening Opacification
Worsening pattern of HMD itself
Congestive heart failure (from PDA or fluidoverload)
Persistent patency of ductus arteriosus
Oxygen stimulus is missing to close ductus
Development of BPD
Superimposed pneumonia (uncommon)
Pulmonary hemorrhage (uncommon)

Day 2
Day 1
Worsening Opacification – Pulmonary Edema
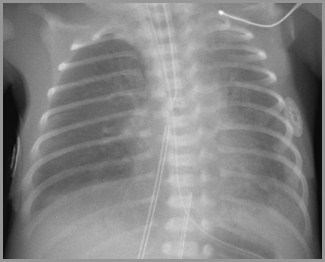
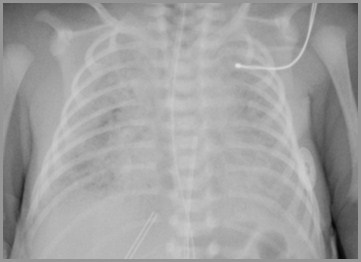

Day 5
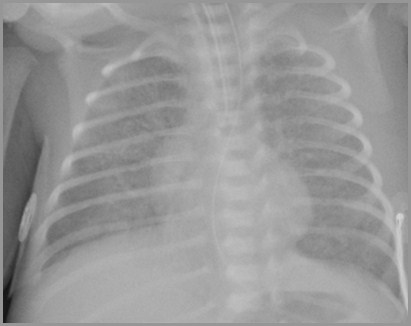
Improving Opacification – Pulmonary Edema

Worsening Opacification – Right Lung Atelectasis
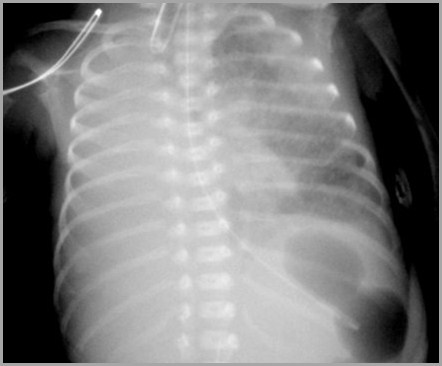

Hyaline Membrane DiseaseChronic Complications
Intracranial hemorrhage andperiventricular leukomalacia
Localized interstitial emphysema
Recurrent respiratory tract infections
Retrolental fibroplasia
Subglottic stenosis from intubation

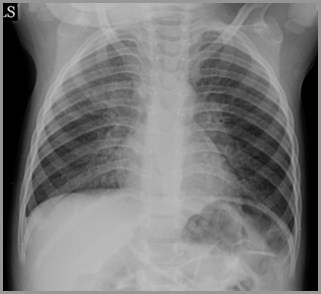

20 mos later
HMD at birth

Becomes evident after increasedpulmonary vascular resistance falls
Suspect PDA in an infant whodeteriorates after initial improvement
1st treated with ibuprofen orindomethacin
If refractory RDS, surgical closure
PDA in HMD

PDA in HMD

Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Chronic RespiratoryInsufficiency of the Premature
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Chronic RespiratoryInsufficiency of the Premature

Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaChronic Respiratory Insufficiency of the Premature
BPD is consequence of early acute lungdisease
BPD may complicate HMD
Also meconium aspiration syndrome andpneumonia
Common to most is oxygenadministered under positive pressure

Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaChronic Respiratory Insufficiency of the Premature
Oxygen requirement at 28 days of life orafter a corrected gestational age of 36weeks to maintain arterial oxygentensions >50 mm Hg accompanied byabnormal chest radiographs
Rarely occurs in infants > 1250 g and ininfants born after 30 weeks gestation

Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaImaging Findings
May be impossible to distinguish early stagesof BPD from later stages of HMD
Coarse, irregular, rope-like, linear densities
Represents atelectasis or fibrosis
Lucent, cyst-like foci
Hyperexpanded areas of air-trapping
Hyperaeration of the lungs

Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia

Fibrosis oratelectasis
Fibrosis oratelectasis

Air-trapping
Air-trapping


Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia

Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia

Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaImaging Findings
Conglomerate disease in BPD
Shifting atelectasis
Episodes of aspiration or pulmonary edema
Superimposed pneumonia
Changes of BPD will revert to normal onthe chest radiograph in most patientsafter the age of two

Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia with Atelectasis

Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia with Atelectasis
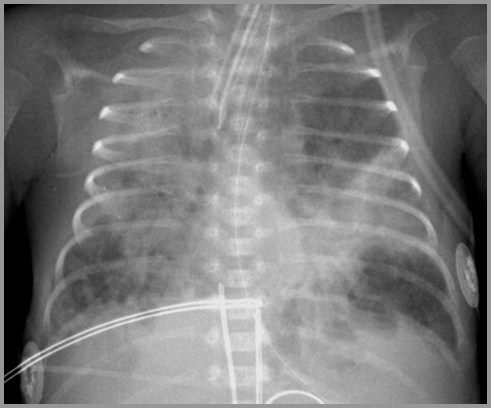

Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaDifferential Diagnosis
Pulmonary interstitial emphysema (PIE) may look similar
Smaller air-containing spaces in PIE (bubbly appearance)
Meconium aspiration may look identical
But history is different (BPD=preemie with chronic dz)
Shunts
Such as a patent ductus arteriosus
Infection
Especially with group A beta streptococci
Congestive heart failure and pulmonary edema

Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaComplications
Sudden infant death
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Increased risk of pulmonary infection
Development of asthma

Transient Tachypneaof the Newborn
Neonatal Retained Fluid Syndrome
Transient Tachypneaof the Newborn
Neonatal Retained Fluid Syndrome

Transient Tachypnea of the NewbornTTN
Usually full-term or slightly preterm
Some delivered by C-section; someprecipitous labor
Mild respiratory distress immediatelyafter birth
Improve within several hours

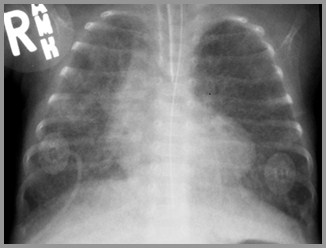
Transient Tachypnea of the NewbornImaging Findings
Hyperinflation of the lungs
Fluid in the fissures
Laminar effusions
Fuzzy vessels

Term infant with respiratory distress
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
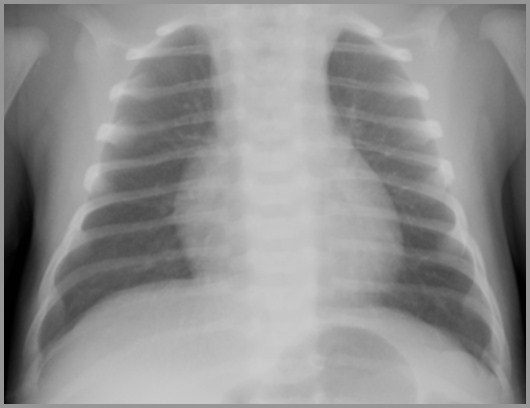
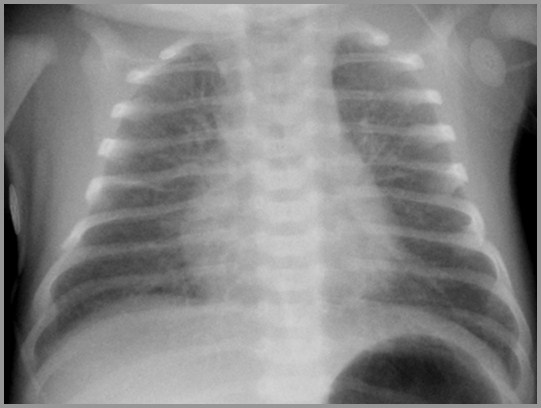

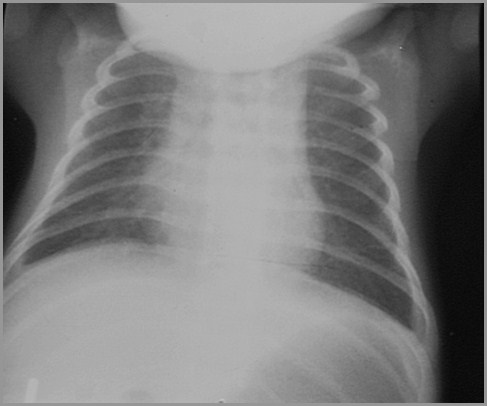
Term infant with respiratory distress
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
IndyRad

Term infant with respiratory distress
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
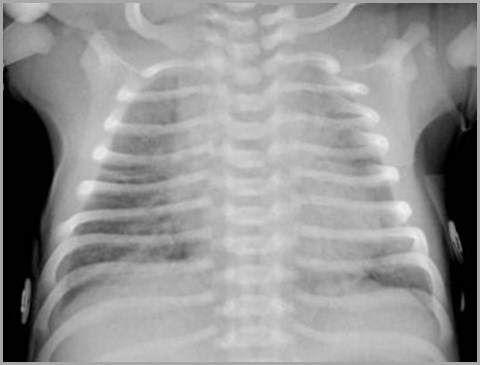

Transient Tachypnea of the NewbornTreatment
Oxygen
Maintenance of body temperature
Improvement most often occurs in < 24 hrs

Transient Tachypnea of the NewbornDifferential Diagnosis of TTN
CHF
TTN appears earlier and clears within < 24 hrs
Neonatal pneumonia
Infant with TTN not as sick; TTN clears rapidly
Meconium aspiration syndrome
Infant with TTN is term and not meconium stained

Meconium AspirationSyndrome
Meconium AspirationSyndrome

Meconium Aspiration SyndromeGeneral Considerations
Most common cause of neonatal respiratorydistress in full-term/postmature infants
Hyaline membrane disease most common cause inpremature infants
Pathogenesis
Meconium in amniotic fluid of 20% of pregnancies
Meconium products produce bronchial obstructionand air-trapping
Chemical pneumonitis

Meconium Aspiration SyndromeClinical Findings
Post-mature
Severe respiratory distress almostimmediately
Respiratory distress more severe thanTTN

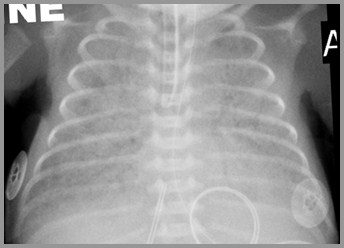
Meconium Aspiration SyndromeImaging Findings
Diffuse “ropey” densities (similar to BPD)
Patchy areas of atelectasis and emphysema from air-trapping
Hyperinflation of lungs
Spontaneous pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum
25%; usually requiring no therapy
Small pleural effusions (20%)
No air bronchograms
Clearing usually quick if mostly water; days-weeks ifmostly meconium

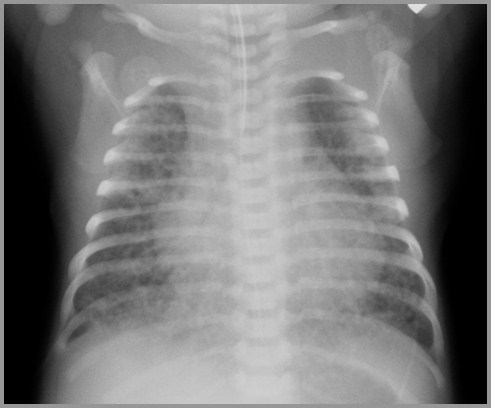
Term infant with respiratory distress
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome

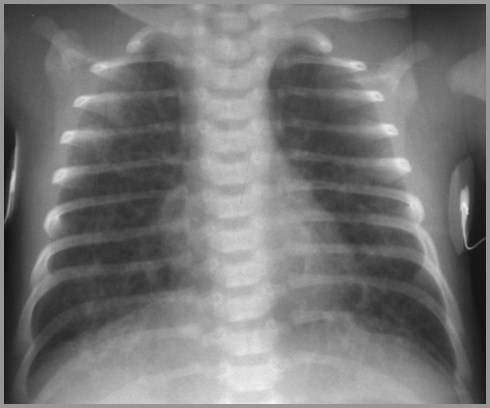
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Term infant with respiratory distress

Meconium Aspiration Syndrome with PTX
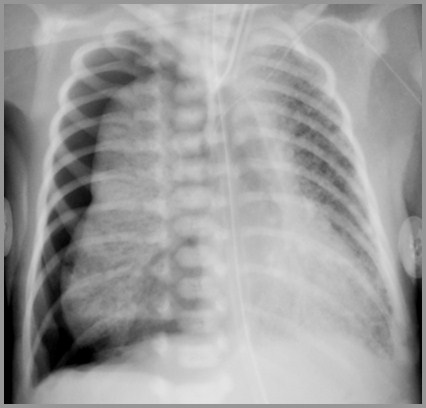

Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Treatment
Supportive
Antibiotics and oxygen
ECMO can be used
Complications
Pulmonary hypertension → R→L shunting
Cyanosis
Anoxic brain damage

Neonatal Pneumonia
Neonatal Pneumonia

Neonatal PneumoniaGeneral Considerations
Etiology
Intrauterine infection or during delivery
Most are bacterial in origin
Group A Beta nonhemolytic Strep usedto be most common
Now E. Coli in preemies

Neonatal PneumoniaClinical Findings
Not febrile
Marked respiratory distress
Tachypnea
Metabolic acidosis
Septicemia and shock

Neonatal PneumoniaImaging Findings
Perihilar streaky pattern may resembleTTN
Patchy airspace disease
Diffuse, relatively homogeneousinfiltrates resembling ground-glasspattern of HMD
Occasionally pleural effusion may occur

Neonatal PneumoniaImaging Findings
Lobar consolidation from infection isunusual in a newborn
Group B Strep looks most like HMD
Term infant with findings of “HMD”should be considered to havepneumonia until proven otherwise

Neonatal PneumoniaTreatment
Appropriate antibiotic
Oxygen
Fluid support as needed

Strep pneumonia
© R3

Streptococcal PneumoniaComplications and Associations
Complications
Bronchiectasis
Lung abscess
Glomerulonephritis
Associated with
Delayed onset of diaphragmatic hernias innewborns

Delayed development of right diaphragmatic hernia
U of Hawaii

Chlamydial Pneumonia
Contamination during delivery
Develops at 2 to 12 weeks of age
Tachypneic but usually not critically ill
Conjunctivitis caused by same organism
X-rays show bilateral interstitial infiltrates
Treatment with erythromycin → rapidresolution

Chlamydia
R3

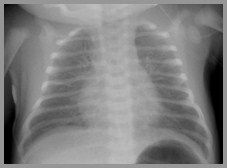
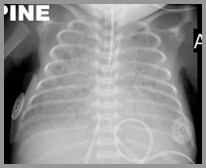
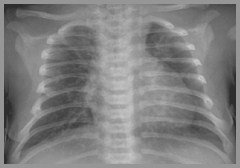
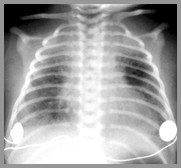
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Transient Tachypnea
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Aeration in Neonatal Lung Disease
Disease
Aeration
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Transient Tachypnea
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia
Under - Over

Aeration in Neonatal Lung Disease
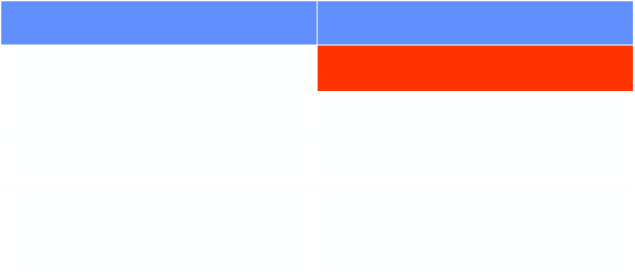
Disease
Aeration
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Under
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Transient Tachypnea
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Aeration in Neonatal Lung Disease
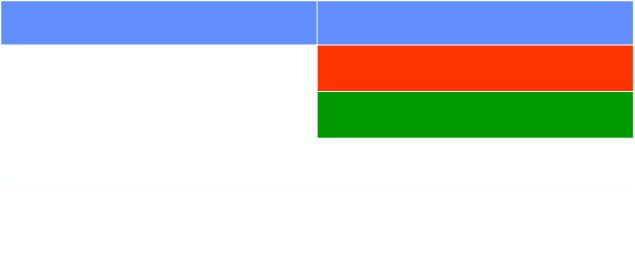
Disease
Aeration
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Under
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Over
Transient Tachypnea
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Aeration in Neonatal Lung Disease
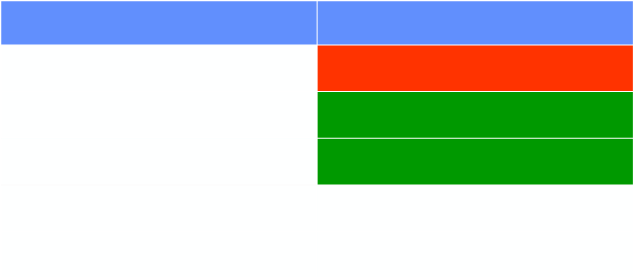
Disease
Aeration
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Under
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Over
Transient Tachypnea
Over
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Aeration in Neonatal Lung Disease
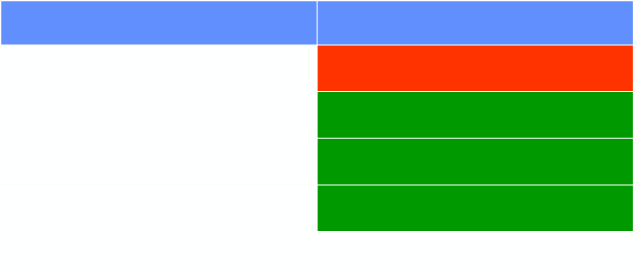
Disease
Aeration
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Under
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Over
Transient Tachypnea
Over
Meconium Aspiration
Over
Neonatal Pneumonia

Aeration in Neonatal Lung Disease
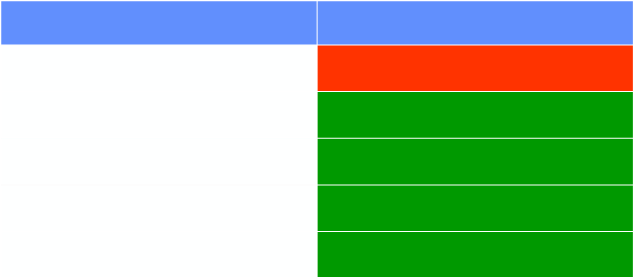
Disease
Aeration
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Under
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Over
Transient Tachypnea
Over
Meconium Aspiration
Over
Neonatal Pneumonia
Over

Descriptive Patterns
Disease
Descriptive pattern
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Transient Tachypnea
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Descriptive Patterns

Disease
Descriptive pattern
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Ground-glass, finely granular
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Transient Tachypnea
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Descriptive Patterns

Disease
Descriptive pattern
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Ground-glass, finely granular
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Cystic lucencies
Transient Tachypnea
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Descriptive Patterns

Disease
Descriptive pattern
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Ground-glass, finely granular
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Cystic lucencies
Transient Tachypnea
Fissural fluid, fuzzy vessels
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Descriptive Patterns

Disease
Descriptive pattern
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Ground-glass, finely granular
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Cystic lucencies
Transient Tachypnea
Fissural fluid, fuzzy vessels
Meconium Aspiration
Coarse, ropey densities
Neonatal Pneumonia

Descriptive Patterns

Disease
Descriptive pattern
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Ground-glass, finely granular
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Cystic lucencies
Transient Tachypnea
Fissural fluid, fuzzy vessels
Meconium Aspiration
Coarse, ropey densities
Neonatal Pneumonia
Perihilar streaking

Effusions in Neonatal Lung Disease

Disease
Effusion
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Transient Tachypnea
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia
Yes – No – Maybe

Effusions in Neonatal Lung Disease

Disease
Effusion
Hyaline Membrane Disease
No
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Transient Tachypnea
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Effusions in Neonatal Lung Disease

Disease
Effusion
Hyaline Membrane Disease
No
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
No
Transient Tachypnea
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Effusions in Neonatal Lung Disease

Disease
Effusion
Hyaline Membrane Disease
No
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
No
Transient Tachypnea
Yes
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

Effusions in Neonatal Lung Disease

Disease
Effusion
Hyaline Membrane Disease
No
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
No
Transient Tachypnea
Yes
Meconium Aspiration
Maybe
Neonatal Pneumonia

Effusions in Neonatal Lung Disease

Disease
Effusion
Hyaline Membrane Disease
No
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
No
Transient Tachypnea
Yes
Meconium Aspiration
Maybe
Neonatal Pneumonia
Maybe

Pre-test Revisited


Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
34 week preemie 6 weeks post-partum


Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
Term infant with respiratory distress; birth

Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn –Day 3

Term infant with respiratory distress; birth


Hyaline Membrane Disease
36 week preemie with respiratory distress; birth


USUHS
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Term infant with respiratory distress; birth


© R3
Neonatal Pneumonia
Term infant with severe respiratory distress; Day 2

More Unknowns

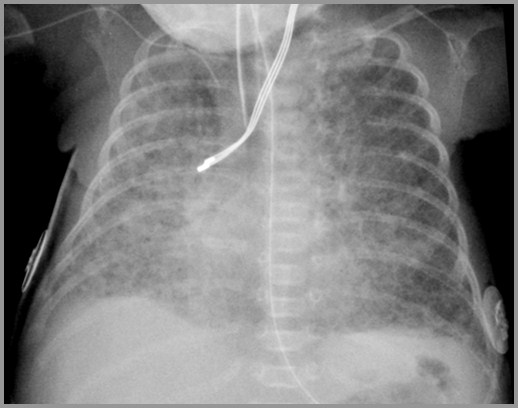
Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema
Premature Infant – Day 3

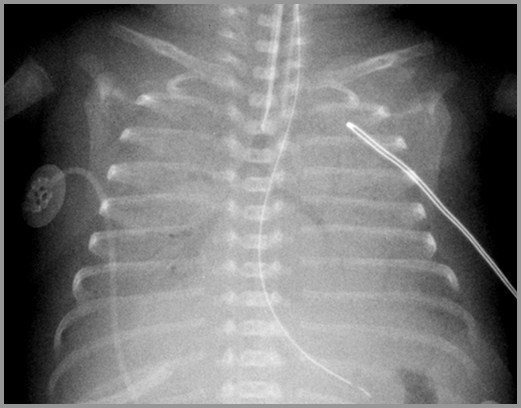
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Premature Infant – Day 2

Term infant with respiratory distress
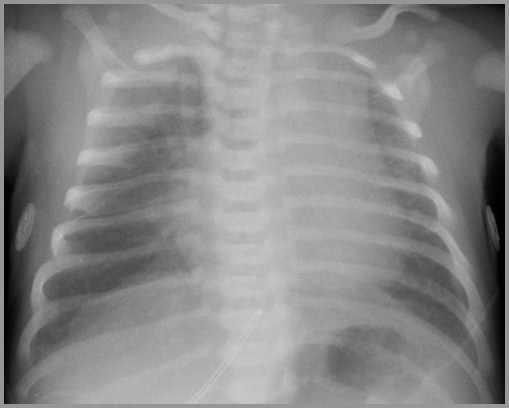

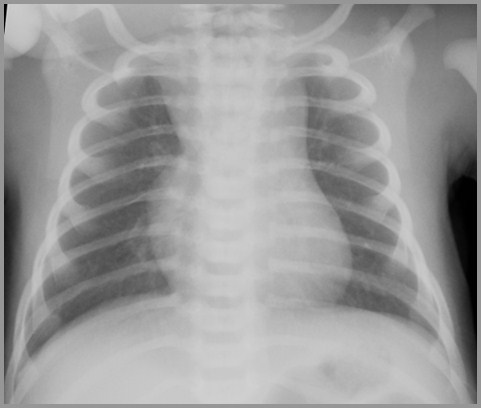
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
Term infant with respiratory distress – 2 days later

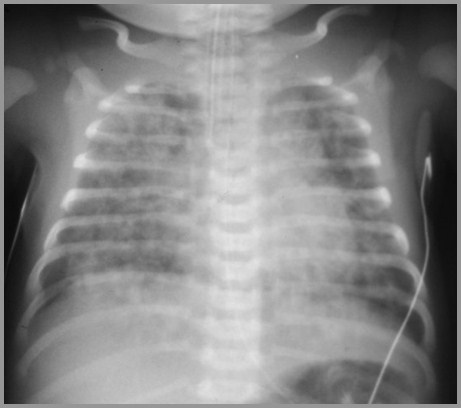
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Newborn with respiratory distress

Neonatal Pneumonia (Strep)
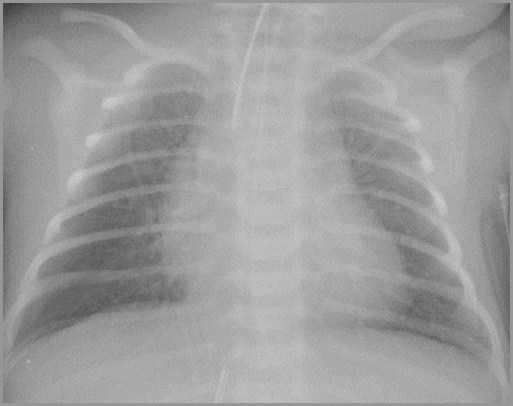
Term infant with severe respiratory distress
PediatricEducation.org

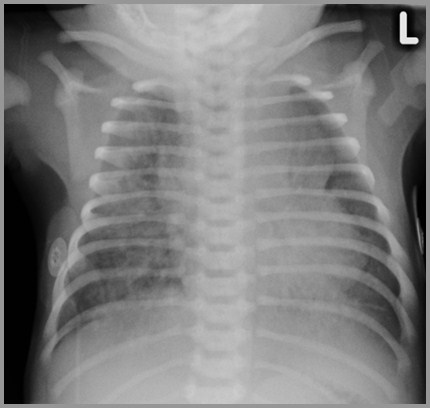
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
41 week newborn with respiratory distress

Hyaline Membrane Disease
Preemie with respiratory distress
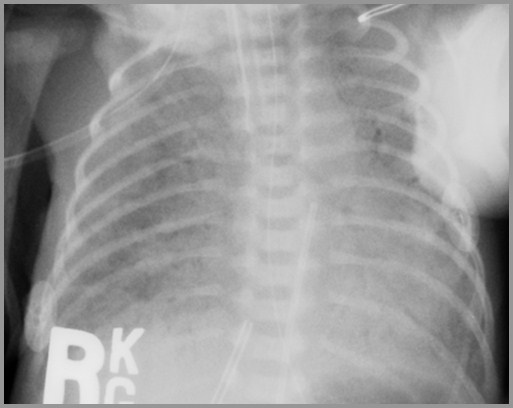






Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Transient Tachypnea
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Meconium Aspiration
Neonatal Pneumonia

The End
The End